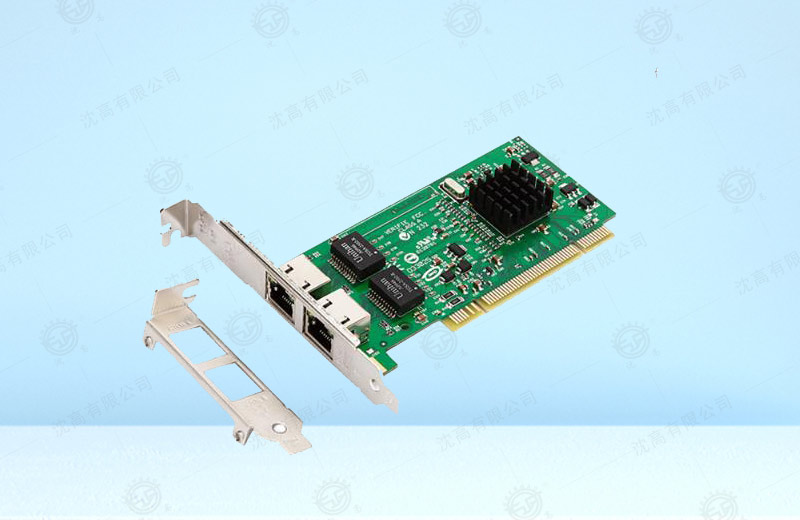
The network card is equipped with processor and memory (including RAM and ROM).Communication between network card and local area network is performed by serial transmission via cable or twisted pair.Communication between network card and computer is carried out in parallel through I/O bus on computer main board.An important function of the network card is therefore to perform a serial/parallel conversion.Since the data rate on the network is different from that on the computer bus, a memory chip that caches the data must be installed in the network card.
Network cards were previously plugged into the computer bus as extension cards, but due to their low cost and the prevailing Ethernet standards, most new computers have integrated network interfaces on the main board.These boards either integrate Ethernet functionality into the main board chip or use a cheap network card connected to the main board via PCI (or an updated PCI-Express bus).Unless multiple interfaces are required or other types of networks are used, a separate network card is no longer required.Even the updated motherboard may contain a built-in dual network (Ethernet) interface.
The device driver for managing the network card must be installed in the operating system of the computer when installing the network card.This driver will then tell the network card where the data blocks transmitted from the LAN should be stored.The network card also has the ability to implement the Ethernet protocol.
The network card is not an independent autonomous unit because it does not have a power supply itself but must use and be controlled by the inserted computer's power supply.The network card can therefore be viewed as a semi-autonomous unit.When the network card receives an error frame, it discards the frame without notifying the computer it has inserted.When the network card receives the correct frame, it uses the interruption to notify the computer and deliver it to the network layer in the stack.When a computer is sending an IP data package, it is sent down by the protocol stack to the network card to be assembled into a frame and sent to the local area network.
With the continuous improvement of integration, the number of chips on network cards is decreasing. Although there are many kinds of network cards produced by different manufacturers, their functions are quite different.