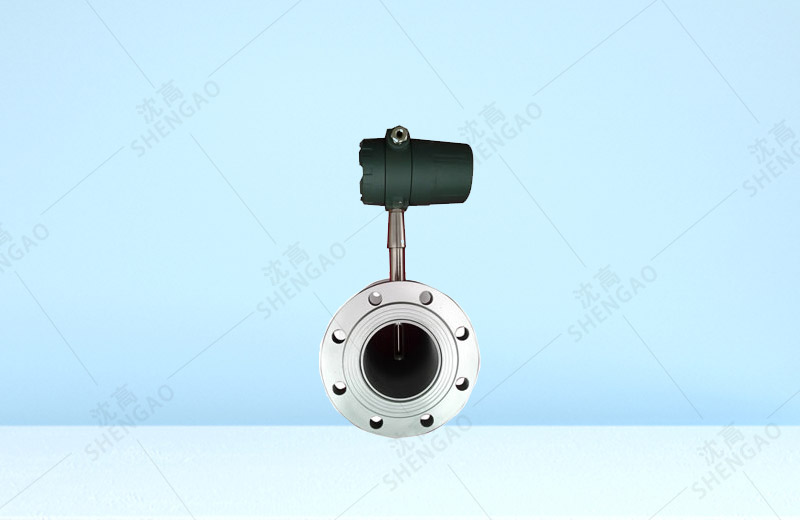
Thermal gas mass flowmeter is an instrument that uses the principle of heat conduction to measure the flow rate. The instrument uses the method of constant temperature difference to accurately measure the mass flow of gas. It has the advantages of small size, high degree of digitalization, convenient installation and accurate measurement. The sensor part consists of two benchmark platinum resistance temperature sensors. With a bridge loop, one sensor measures the flow temperature and the other maintains a thermostatic difference above the fluid temperature, allowing flow measurements under high temperature and pressure conditions. The thermal gas mass flowmeter has the following technical advantages:
● The real mass flowmeter, the gas flow measurement without temperature and pressure compensation, measurement is convenient and accurate. The mass flow rate or standard volume flow rate of the gas can be obtained.
● Wide range ratio, can measure the flow rate up to 100Nm/s bottom to 0.5nm /s gas, can be used for gas leak detection.
● Good seismic performance and long service life. The sensor has no moving parts and pressure sensing parts and is not affected by vibration to the measurement accuracy.
● Easy installation and maintenance. If site conditions permit, installation and maintenance without stopping production can be realized.
● Digital design. The whole digital circuit measurement, accurate measurement, easy maintenance.
● The use of RS-485 communication, or HART communication, can achieve factory automation, integration.
Working principle
The sensor part of the thermal gas mass flowmeter is composed of two precise platinum thermal resistors. The resistor is encapsulated in stainless steel tube, and does not directly contact with fluid medium, but it has good heat transfer performance. One of the shorter is a medium temperature sensing element; The other is the heating element. As gas flows through the heating element. Take the heat away. The amount of heat removed is proportional to the flow rate and density of the fluid. The flowmeter consists of two temperature sensors. A certain amount of heating power P is applied to one of the sensors. Increase its temperature to the measured value of T2. The other sensor measures the gas temperature T1. The mass flow rate of the gas can be determined according to the temperature difference between the heater sensor and the gas (△T2T1) and the heating power P.
This is called King's law. Depend on sensor geometry and gas characteristics such as thermal conductivity, viscosity, and specific heat capacity.
The values of these coefficients are specific to the flow meter and gas, so the ITMF meter must be calibrated for the gas to be measured. In practical application, there are two ways to measure gas mass flow: constant power method or constant temperature difference method.
In order to maintain a fixed temperature difference between TS and TA, the circuit must provide more power to the heating element. The output power of the circuit is directly related to the mass flow of the fluid, and the corresponding mass flow can be obtained by measuring the output power of the circuit. Because the heat on the heating element is mainly taken away by the flow of gas molecules, rather than the effect of heat conduction. Therefore, the flow meter is almost independent of the composition of the fluid within a certain range of working conditions.